Structure & thermodynamics of polymer mixtures
The Random Phase Approximation (RPA) describes remarkably well the structure factor of homogeneous polymer mixtures, even highly interacting or with seriously asymmetric monomers. Phase separation via spinodal decomposition is reasonably well described by the Cahn-Hilliard theory, provided that the "early stage" is observable (ie, very close to the spinodal line, slow polymer dynamics).
Dynamics of bulk polymers and blends
Elastic scans of homopolymers
References
H. Gerard, J. T. Cabral and J. S. Higgins, "Flow-induced enhancement of concentration fluctuations in polymer mixtures", Phil. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. A 361, 767 (2003).
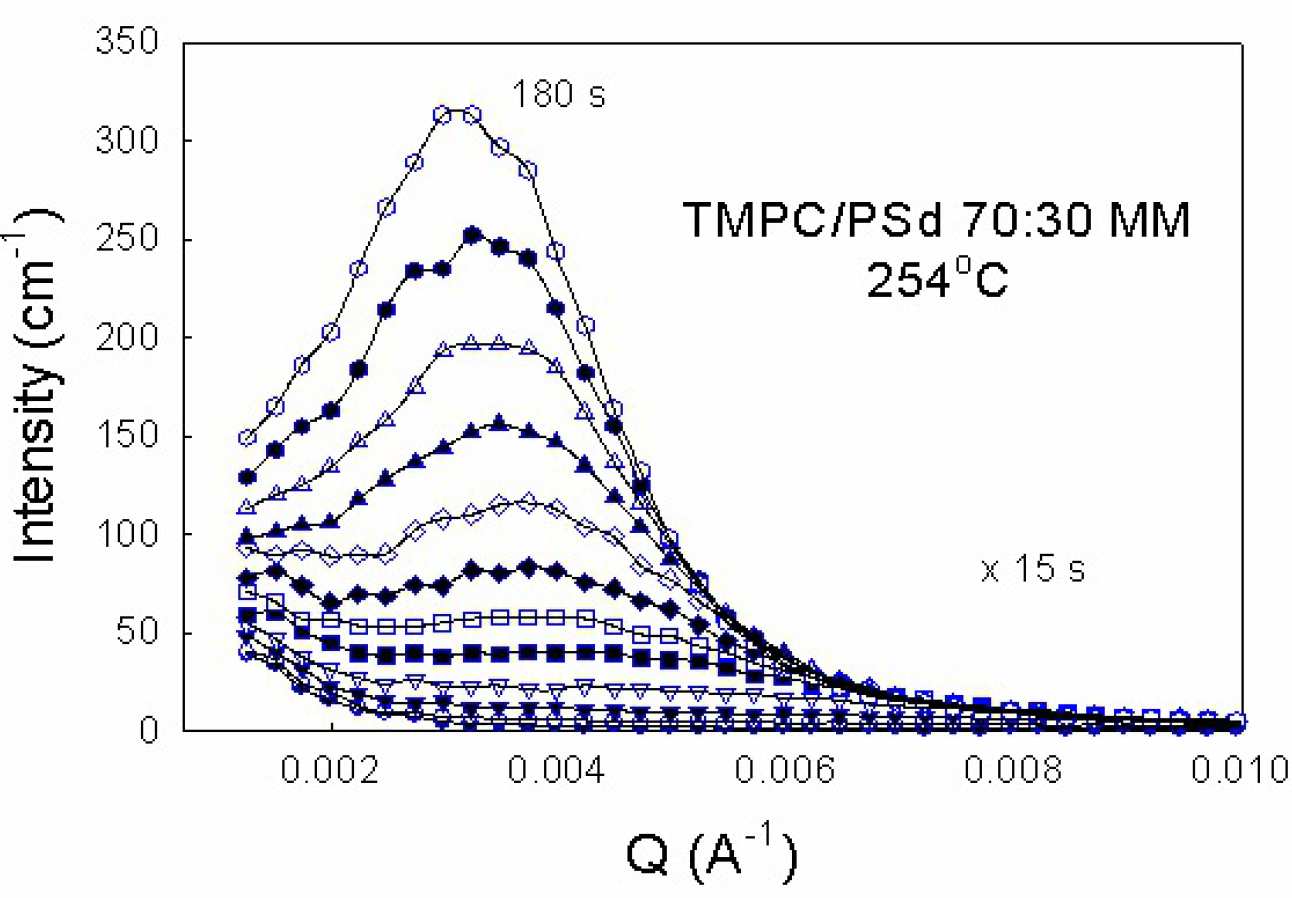
J. T. Cabral, H. Gerard, N. Clarke, and J. S. Higgins, "Phase separation of polymer blend TMPC/PS: dependence on blending method", Physica B 276-278, 408 (2000).
J. T. Cabral, A. Luzar, J. Teixeira, and M.-C. Bellissent Funel, "Water dynamics in DMSO-water mixture",Physica B 276-278, 508 (2000).
J. T. Cabral, A. Luzar, J. Teixeira, and M.-C. Bellissent Funel, "Single-particle dynamics in DMSO-water eutectic mixture by neutron scattering", J. Chem. Phys. 113, 8736 (2000).