Modern measuring systems can easily produce data sets consisting of thousands, even millions of points.
The data points are almost always random.
Also, accurate modelling of shapes using NURBS often involves surfaces with tens of thousands of control points.
The developed surface approximation method was designed to address such situations. Using the cloud of points and a suitable base surface as input, the process involves the following iterative steps:
- Data parameterisation (assigning UV coordinates to data points)
- Linear Least Squares fitting
- Knot insertion
Knot insertion is usually necessary in order to introduces additional control points and to provide additional flexibility for modelling the surface detail. The iterative process may be applied a number of times until satisfactory modelling accuracy is achieved.
The described process is known to suffer from two main issues, which have been successfully resolved.
NURBS
- Relative sparsity of data points in relation to the control points can lead to ill-conditioning or even instability. This is often the case following knot insertion.
- Solved through the use of suitable smoothing criteria, which also allow good user control over the surface regions poorly defined by the data.
Consider the example of fitting a flat base surface to non-uniformly distributed data

Successive steps of knot insertion and fitting lead to ill-conditioning in sparsely sampled regions
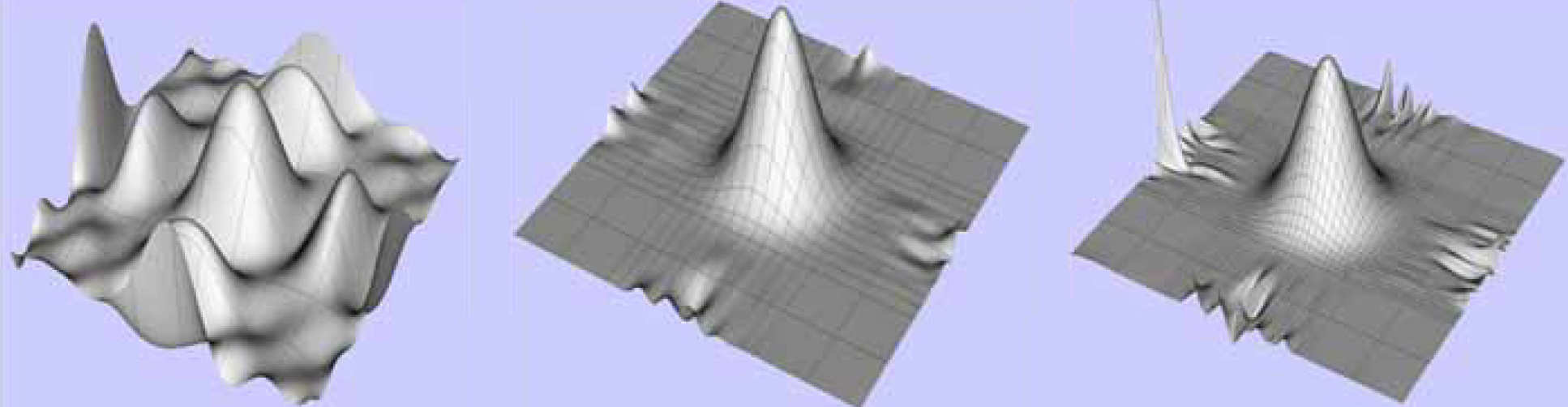
Resolved using the implemented smoothing criteria
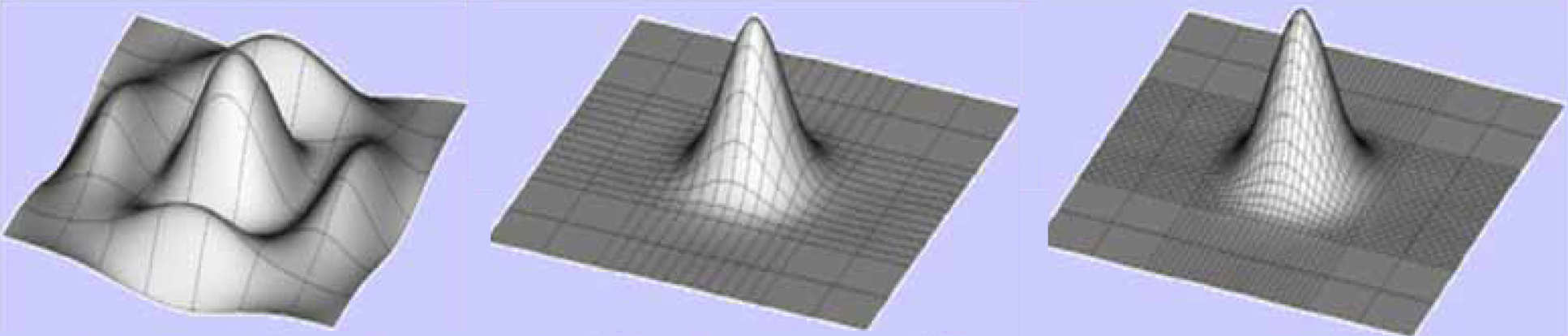
- Large number of data points and control points can quickly lead to problems of insoluble size in terms of both memory and computational time
- Solved by identiftying and fully exploiting the exact sparsity structure of relevant matrices
- Realised computational complexity:
- Memory storage linear with the number of control points
- Computing time linear with the number of data points
The following data illustrates the realised performanace of the method on a modest Pentium PC (1GHz, 1Gb).
- Number of data points: 1,000,000
- Number of control points: 10,000
- Total memory requirement: 1,054 KB
- Preparation time (setting up normal equationa): 57 seconds
- Solution time (per iteration): 233 seconds
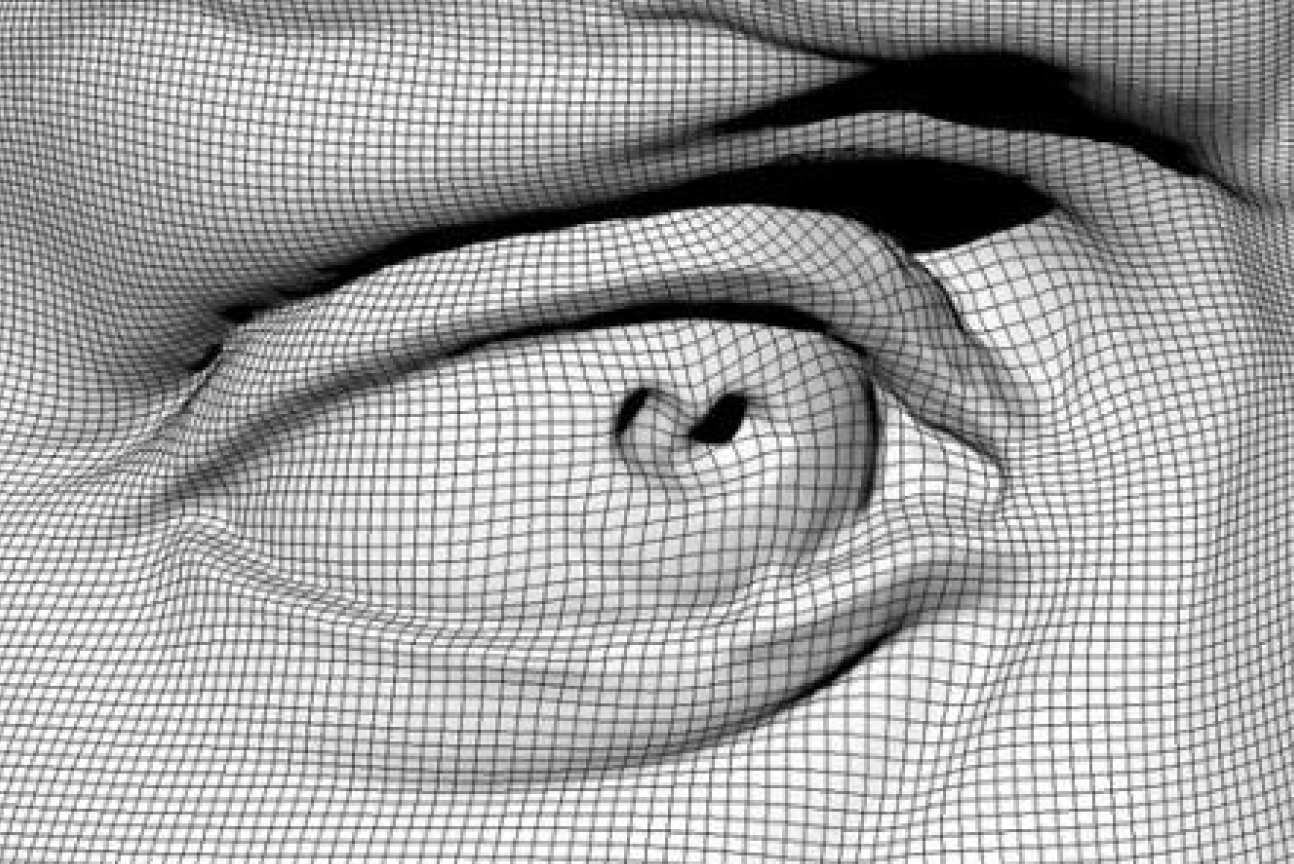
Surface reconstruction from digitsed data
The pictures show reconstructed face of the statue of David (courtesy of the Digital Michelangelo Project). 500,000 points were obtained using laser scanner and the surface was reconstructed using 120,000 control points in iorder to accurately represent the fine detail.

Simplification of CAD models
The pictures show a CAD model of a calculator. The original model consisted of several hundred trimmed NURBS patches. The model was sampled at a high density and a single wraparound NURBS surface was fitted to the data. This is important in many applications where dealing with a large number of trimmed surface antities (possibly with gaps and overlaps) causes difficulties in downstream processing, e.g. automatic meshing.
Contact us
Dr. Mihailo Ristic
Senior Lecturer
T: +44 (0)207 594 7048
E: m.ristic@imperial.ac.uk
Dr. Djorje Brujic
Research Fellow
T: +44 (0)207 594 7175
E: d.brujic@imperial.ac.uk