Contact us
For any enquiries related to Microvesicles in Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome, please contact
Dr Sanooj Soni
s.soni@imperial.ac.uk
What we do
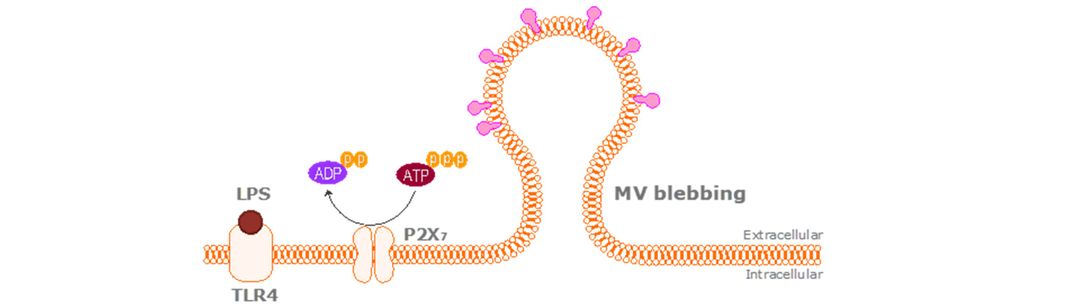
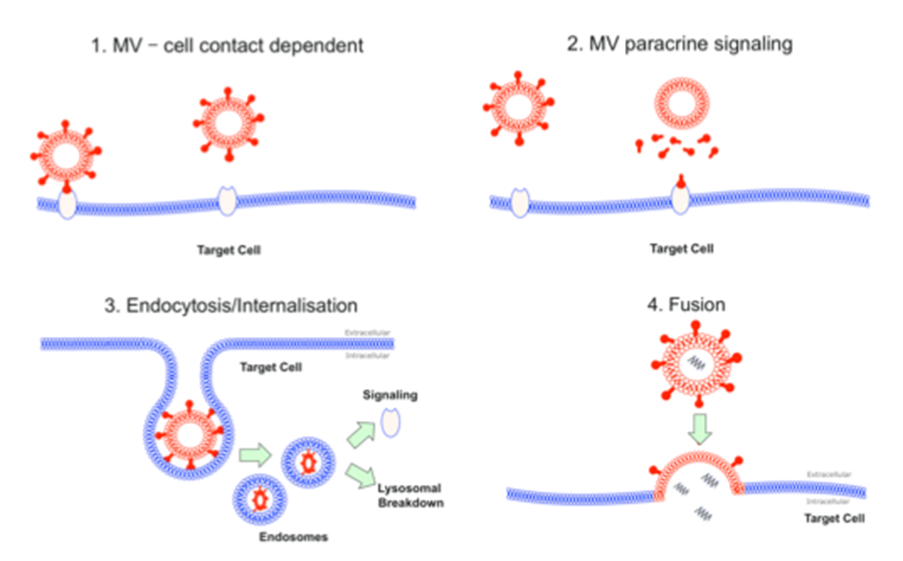
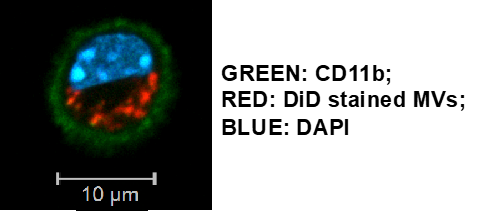
We investigate the propagation of lung injury and in critically unwell patients and peri-operative patients. This has predominantly focused upon the role of microvesicles in acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). Our group is primarily interested in cellular communication and the transfer of inflammatory cargo/milieu between alveolar and pulmonary cells during lung injury as well as pulmonary cells to peripheral organs. We are also currently exploring the role of MVs in COVID-19 induced ARDS and multi-organ failure.
Why it is important
ARDS
Patients with ARDS have a high mortality and consume considerable healthcare resources due to severity of illness and long intensive care stays. Despite intense research, there are no disease modifying therapies for ARDS. There remains an urgent, unmet need for a re-direction in ALI research to identify novel therapeutic targets, which may lead to new treatments.
Perioperative
Each year, over 310 million major surgical cases are performed worldwide with 2.4 million general anaesthetics administered in the UK alone. Postoperative pulmonary complications (PPCs) occur in up to 33% of cases, significantly increasing short- and long-term mortality and morbidity, and hospital length of hospital stay with its attendant costs. Among various potential causes of PPCs, mechanical ventilation, used during peri- and/or post-operative period with major surgery, is a major contributing factor, as it often produces unphysiological alveolar stretch instigating lung inflammation and injury, a pathophysiology termed as ventilator-induced lung injury (VILI). Our understanding of the mechanisms underpinning the pathophysiology of VILI is still primitive resulting in a lack of effective treatments and subsequent poor outcomes.
COVID-19
A significant proportion of hospitalised patients with COVID-19 require intensive care due to ARDS (ARDS) and multi-organ failure (MOF). Indeed, 51.8% COVID-19 ARDS patients develop acute kidney injury (AKI), which has a mortality of 61%. Management remains principally supportive and there remains an urgent need for research investigating mechanisms of respiratory/kidney failure in COVID-19 to identify novel diagnostic/therapeutic targets.
Funders and collaborators
Funders
Researchers
Dr Sanooj Soni
/prod01/channel_3/media/images/people-list/Sanooj-Soni.jpeg)
Dr Sanooj Soni
Professor Masao Takata
/prod01/channel_3/media/images/people-list/Professor-Masao-Takata.jpeg)
Professor Masao Takata
Dr Michael Wilson
/prod01/channel_3/media/images/people-list/Dr-M-Wilson.jpg)
Dr Michael Wilson
Dr Kieran O'Dea
/prod01/channel_3/media/images/people-list/K-O'dea-(1).jpg)
Dr Kieran O'Dea
Dr Yoichi Iki
/prod01/channel_3/media/images/people-list/No-Pic-portrait-reformated.jpg)
Dr Yoichi Iki
Miss Dane Cheng
/prod01/channel_3/media/images/people-list/No-Pic-portrait-reformated.jpg)
Miss Dane Cheng
Miss Sehar Khushi
/prod01/channel_3/media/images/people-list/No-Pic-portrait-reformated.jpg)
Miss Sehar Khushi
PhD students
Dr Jonathan Stevens
/prod01/channel_3/media/images/people-list/No-Pic-portrait-reformated.jpg)
Dr Jonathan Stevens
Miss Diane Cheng
/prod01/channel_3/media/images/people-list/No-Pic-portrait-reformated.jpg)
Miss Diane Cheng