Imperial team are gearing up for their mission to the sun
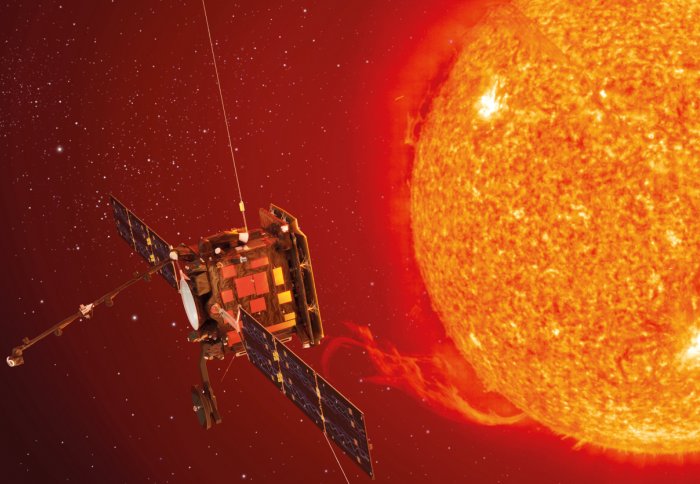

A NASA rocket is expected to blast off from Cape Canaveral in October 2018, carrying a spacecraft that will fly closer to the sun than ever before.
The spacecraft, known as Solar Orbiter, is aiming to answer questions about the heliosphere – a bubble of gas that fills the entire solar system. The gas is made of very hot plasma that comes off the upper atmosphere of the sun, known as the solar wind. The Solar Orbiter mission is hoping to provide new insights into how the sun makes the solar wind and how this wind affects the wider solar system.
On board for the seven year mission will be an instrument known as a magnetometer, designed and built by researchers from the Space and Atmospheric Physics group at Imperial College London, which will measure the sun’s magnetic field. Solar Orbiter researchers need to investigate the magnetic field because it plays a key role in creating the solar wind and in determining the behaviour of the particles as they flow away from the sun.
The Imperial team recently sent a test model of their magnetometer to Airbus Defence and Space in Stevenage, where the Solar Orbiter spacecraft is being put together. This week, engineers there switched on the model magnetometer to begin testing its ability to communicate with the rest of the spacecraft.
Before the researchers sent off their model for testing, they let us look around their lab to see the work they are doing to get the magnetometer ready for its mission. The photos below show the model magnetometer and Imperial’s Solar Orbiter team at work (photos by College photographer Thomas Angus).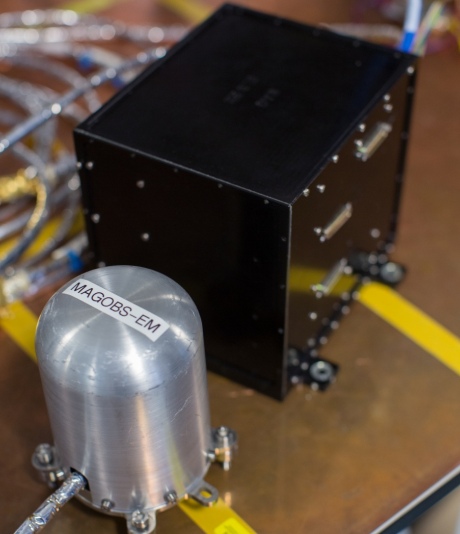
The magnetometer is made up of two sensors (silver instrument, left); a black box containing electronics, a computer processor and a power supply; and cables to provide power and communications to the sensors.

Helen O’Brien is the lead engineer on the project. The magnetometer is being designed to withstand the huge vibrations of the launch rocket as well as extremes of heat and cold.
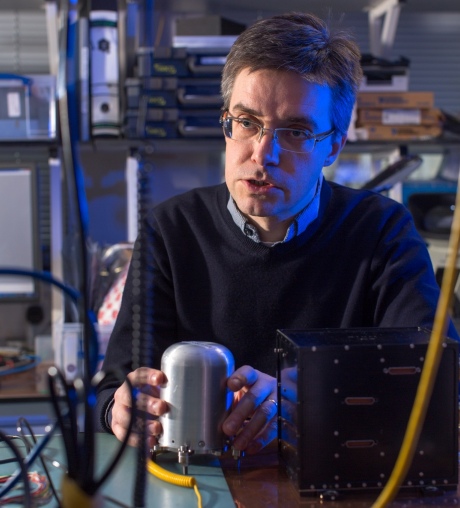

The sensor, held here by Principal Investigator Professor Tim Horbury, will measure the sun’s magnetic field. Two sensors will be mounted on a 3m-long boom behind the Solar Orbiter craft, far enough away to minimise interference from the spacecraft and its instruments. The sensors will be wrapped in specially designed thermal blankets to protect them from the extreme cold that they will experience as a result of being situated behind the spacecraft's heat shield. 
Once the Solar Orbiter goes into its orbit around the sun, the magnetometer will be able to send back data like this about the sun’s magnetic field.

Trevor Beek, another member of the project team, has been using a powerful microscope to guide him as he carries out intricate soldering work on electronic components on the magnetometer.
Members of the magnetometer team at work in the lab (l-r): Jose A Mateos Dominguez, Helen O’Brien, Maciej Bendyk, Trevor Beek, Lawrence Soung Yee.
Solar Orbiter is a European Space Agency (ESA) mission; the artist's impression of Solar Orbiter is reproduced courtesy of ESA - C. Carreau.
Article supporters
Article text (excluding photos or graphics) © Imperial College London.
Photos and graphics subject to third party copyright used with permission or © Imperial College London.
Reporter
Laura Gallagher
Communications Division