For cells, some shapes are easier to swallow than others
Scientists have probed the process that allows cells to swallow up particles, finding that some shapes are easier to swallow than others.
Cells take in small particles and other objects such as bacteria in a process called engulfment. Single-celled organisms use engulfment to take in food, while in humans it forms the first line of immune system defence, as white blood cells engulf harmful bacteria and other foreign bodies.
Our technique paves the way for models closer to reality, with the dual advantage of understanding bacteria’s defence mechanisms and aiding drug design.
– Dr Robert Endres
In a new study, researchers at Imperial College London and the University of Exeter have used a simple model to investigate how the basic shapes of particles and bacteria can affect how easily they are engulfed by cells.
This could help when designing the optimal shape for drugs, helping them to be more easily taken up by target cells. It could also help explain why some bacteria are especially good at avoiding being engulfed. The results are published today in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
During engulfment, the membrane is pushed out and reaches around the foreign particle, enveloping it and pulling it into the cell to be broken down. Until now, models of this process imagined the particle as a simple sphere, despite the wide range of different particle and bacteria shapes found in nature.
The new model reveals that the easiest shapes to engulf are rod shapes and ovals – but only if they are approached by the cell end-on. On their side, they become more cumbersome. The most difficult shapes to engulf are hourglass-types that can be created, for example, by bacteria dividing while being engulfed. These shapes appear to get stuck and are not fully engulfed.
Co-author Dr Robert Endres from Imperial’s Department of Life Sciences said: “Engulfment is difficult to observe experimentally as immune cells don’t like the laser light we usually use for imaging, which is why only simple spheres have been used in theoretical models so far.
"However, our technique paves the way for models closer to reality, with the dual advantage of understanding bacteria’s defence mechanisms and aiding drug design.”
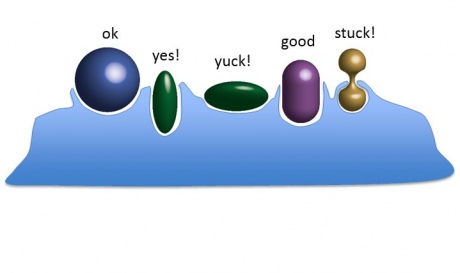
How easily different basic shapes can be engulfed
The team’s model combines two crucial elements. The first is a mathematical model of an expanding membrane cup shape that closely resembles models describing the freezing of water into ice, mathematically known as the supercooled Stefan problem.
The other is information about the active process that cells employ when engulfing particles. When a harmful object enters the body, the immune system emits signalling molecules. The model takes account of how these molecules help guide the bending of the membrane around the shape.
Co-author Dr David Richards, now at the University of Exeter, said: "This study tells us how the shape of bacteria affects how easily our immune cells can destroy them. The shape of some bacteria might make them extremely difficult for the body to destroy, which could be deadly.
"This work could be useful in the pharmaceutical industry, as it might pave the way to novel designs for very small drug-carrying particles that the body cannot accidentally destroy."
The team hopes to expand their simple model to actual bacteria and engineered drug particles with wide-ranging material properties.
-
'Target shape dependence in a simple model of receptor-mediated endocytosis and phagocytosis' by D Richards and R Endres is published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
Article text (excluding photos or graphics) © Imperial College London.
Photos and graphics subject to third party copyright used with permission or © Imperial College London.
Reporter
Hayley Dunning
Communications Division