Mysterious molecular phenomenon could boost precision of targeted drug delivery
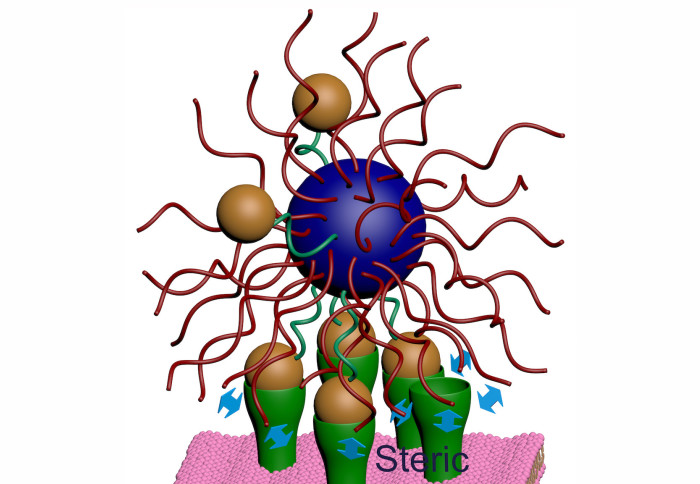
Nanoparticle (blue) coated with ligands (orange) interacting with a receptor (green)-coated surface
Scientists have shown how a type of cellular binding could help pave the way for highly targeted therapies against diseases like cancer.
A growing area of medicine looks at how cellular binding observed in nature – where molecules like viruses or proteins bind to specific receptors on a cell – can be mimicked to aid drug delivery.
The key to unlocking highly targeted drug therapies could lie in directing drug carriers towards cells with a precise number of receptors. Dr Stefano Angioletti-Uberti Department of Materials
Those developing targeted drug therapies aim to recreate this precise binding to develop nano-sized drug carriers that attach only to diseased cells. Once attached, these carriers would release their therapeutic load without affecting healthy cells. If drugs can be specifically targeted in this way, treatments would cause far fewer side effects.
One way to identify which cells are diseased is the number of receptors they express. Cancer cells, for example, tend to express more certain types of receptor than healthy cells.
Now, in a multi-centre collaboration led by Imperial and UCL, researchers have demonstrated how a mysterious molecular concept that the authors dubbed ‘range selectivity’ could be used to target diseased cells with high specificity.
Range selectivity, until now a mysterious phenomenon, is where molecules called ligands attach only to cells whose number of receptors reach a certain threshold.

Senior author and principal investigator Dr Stefano Angioletti-Uberti of Imperial’s Department of Materials, said: “I came across the concept of range selectivity completely by accident. During my theoretical investigation of receptor-ligand binding I noticed that ligands weren’t attaching above a certain threshold of receptor density and had my team re-check our code before realising it wasn't a bug.”
In nature, range selectivity happens because of a balance of attractive and repulsive forces at the molecular level. Past a certain threshold the repulsive force must outweigh the attractive, and so binding is far less likely to take place. This is due to certain physical properties of ligand-receptor interactions.
Following their realisation, the group at Imperial used statistical mechanical modelling to show how modifying certain parameters could tune the balance of attractive and repulsive forces. This provided a ‘molecular handle’ to tune the upper and lower limit of the selectivity range. Their colleagues at UCL, led by Professor Giuseppe Battaglia, then confirmed these theoretical predictions using experimental data.

The results are published in Nature Communications and include contributions from Beijing University of Chemical Technology, the Institute of Physics in Beijing and the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia.
Dr Angioletti-Uberti said: “The key to unlocking highly targeted drug therapies could lie in directing drug carriers towards cells with a precise number of receptors.
“If we can find out which receptor densities are specific to different diseases and apply what we’ve demonstrated to drug carriers, we could treat those diseases effectively with fewer side effects.”
Cancer clues
Could it be that tumour cells’ receptor densities fall outside the range toward which immune cells are programmed to target? Dr Stefano Angioletti-Uberti Department of Materials
Alongside drug targeting, the researchers say their work offers an important insight that could change the way future studies in this field are conducted. For example, researchers could now take into account that simply increasing the number of receptors does not necessarily increase the probability of binding, and in fact may cause it to significantly decrease.
It also offers clues that could go some way to explain why tumours evade attack from the immune system.
Dr Angioletti-Uberti said: “Could it be that tumour cells’ receptor densities fall outside the range toward which immune cells are programmed to target?”
The authors are now looking into how to optimise receptor density on cells to ensure maximum binding, as many parameters like receptor and ligand type can affect the strength of these bonds.
Dr Angioletti-Uberti added: "Nature might already be using this form of binding to its own advantage, or indeed our disadvantage. Understanding this fully could lead to a wealth of disease-targeting possibilities.”
“Combinatorial entropy behaviour leads to range selective binding in ligand-receptor interactions” by Meng Liu, Azzurra Apriceno, Miguel Sipin, Edoardo Scarpa, Laura Rodriguez-Arco, Alessandro Poma, Gabriele Marchello, Giuseppe Battaglia & Stefano Angioletti-Uberti. Published 24 September 2020 in Nature Communications.
Images:
Main - Angioletti-Uberti et al.
Targeted cell - Shutterstock
Cells under manipulation - Angioletti-Uberti et al.
Article text (excluding photos or graphics) © Imperial College London.
Photos and graphics subject to third party copyright used with permission or © Imperial College London.
Reporter
Caroline Brogan
Communications Division