A Tutorial for Bioimpedance Sensors
Our Hamlyn researcher published a tutorial for bioimpedance sensors, aiming to provide a general guidance for electrical bioimpedance sensor research.
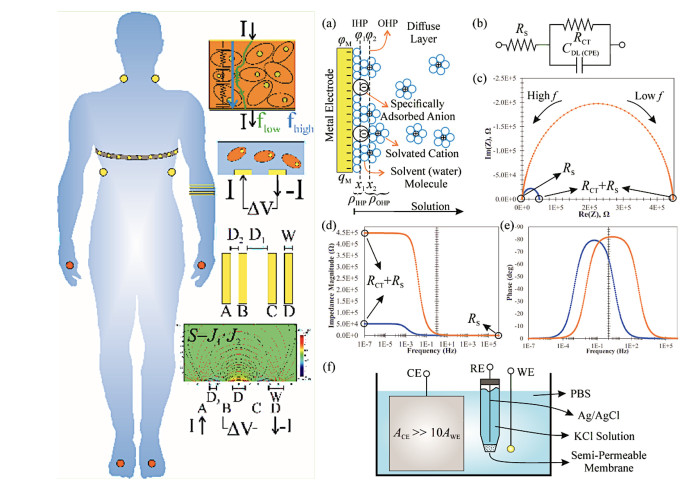
Electrical bioimpedance is a powerful noninvasive technique for characterising tissue and monitoring the evolution of their parameters over time. In other words, it entails the measurement of the electrical properties of tissues as a function of frequency. It is thus a spectroscopic technique.
Electrical bioimpedance has therefore been applied in a plethora of biomedical applications for diagnostic and monitoring purposes. Bioimpedance sensor design must be optimised based on the requirements of the application.
In view of this, our researcher at the Hamlyn Centre published a tutorial for bioimpedance sensors, aiming to provide a general guidance for electrical bioimpedance sensor research.
In this tutorial, the basics of electrical bioimpedance sensor design is discussed. The electrode/electrolyte interface is thoroughly described. The methods for electrode/electrolyte modelling with equivalent circuits and computational tools are also presented.
Moreover, the design optimisation and modelling of bipolar and tetrapolar bioimpedance sensors is illustrated in detail, based on the sensitivity theorem. Analytical and numerical modelling approaches for electric field simulations based on conformal mapping, point electrode approximations and the finite element method (FEM) are also elaborated.
Finally, current trends on bioimpedance sensors are discussed followed by an overview of instrumentation methods for bioimpedance measurements, covering aspects of voltage signal excitations, current sources, voltage measurement front-end topologies and methods for computing the electrical impedance.
This research was supported by EPSRC Programme Grant “Micro-robotics for Surgery (EP/P012779/1)” (Panagiotis Kassanos, "Bioimpedance Sensors: A Tutorial", IEEE Sensors Journal, September 2021).
Article supporters
Article text (excluding photos or graphics) © Imperial College London.
Photos and graphics subject to third party copyright used with permission or © Imperial College London.
Reporter
Erh-Ya (Asa) Tsui
Enterprise