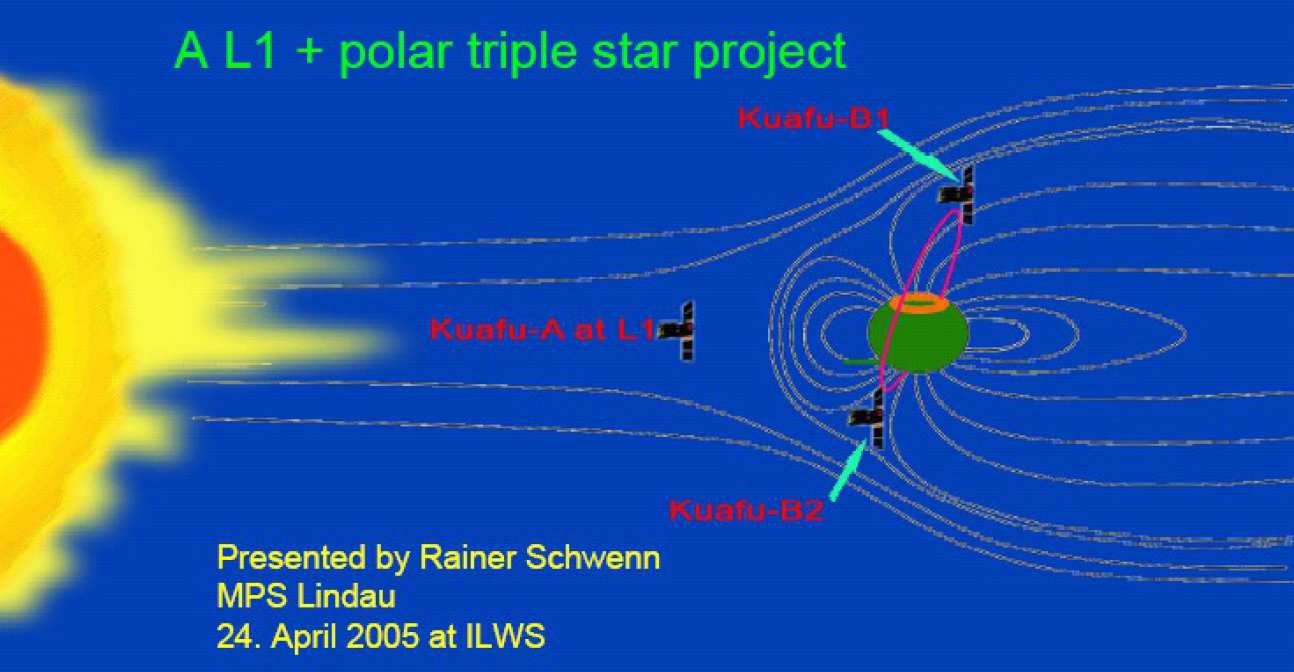
 KuaFu is the first mission dedicated to the study of space weather from its initiation at the Sun to the deposition of energy in the Earth's atmosphere. The mission consists of three spacecraft, one (KuaFu-A) at the L1 Lagrange point between the Earth and the Sun, and two more (KuaFu-B) in polar orbit around the Earth. KuaFu-A will carry a suite of instruments to observe the solar atmosphere, including the initiation of Coronal Mass Ejections (CMEs) and other releases of energetic particles, plasma, and fields, that will impact the Earth. KuaFu-A also carries a set of in situ instruments, including a magnetometer led by SPAT, that will measure directly the particles and fields an hour before they hit the Earth's magnetosphere. The KuaFu-B spacecraft will provide the first continuous imaging of the auroral regions, thereby enabling a cradle to grave capture of space weather storms and events. The KuaFu-B spacecraft also carry a suite of in situ instruments to measure directly the particles and fields, enabling the physical processes responsible for the energy deposition to be studied. SPAT leads the magnetometer investigations on the two KuaFu-B spacecraft.
KuaFu is the first mission dedicated to the study of space weather from its initiation at the Sun to the deposition of energy in the Earth's atmosphere. The mission consists of three spacecraft, one (KuaFu-A) at the L1 Lagrange point between the Earth and the Sun, and two more (KuaFu-B) in polar orbit around the Earth. KuaFu-A will carry a suite of instruments to observe the solar atmosphere, including the initiation of Coronal Mass Ejections (CMEs) and other releases of energetic particles, plasma, and fields, that will impact the Earth. KuaFu-A also carries a set of in situ instruments, including a magnetometer led by SPAT, that will measure directly the particles and fields an hour before they hit the Earth's magnetosphere. The KuaFu-B spacecraft will provide the first continuous imaging of the auroral regions, thereby enabling a cradle to grave capture of space weather storms and events. The KuaFu-B spacecraft also carry a suite of in situ instruments to measure directly the particles and fields, enabling the physical processes responsible for the energy deposition to be studied. SPAT leads the magnetometer investigations on the two KuaFu-B spacecraft.
